How Smart City Forms New Era of Urban Environment
Smart Cities: Problems, Solutions, Technology, and Positive Impact
As the world urbanises rapidly, cities face mounting challenges like traffic congestion, pollution, crime, and public safety risks. In response, the concept of “smart cities” has emerged, leveraging advanced technology to enhance urban life, improve efficiency, and address pressing issues.
Defining Smart Cities
Smart cities represent a transformative phenomenon in urban development. It combines advanced technology, data-driven insights, and sustainable practices to improve the quality of life for residents, enhance city management, and ensure environmental responsibility.
Citizen-centric design is a key principle in the development of smart cities. Emphasising that technology and urban planning should primarily serve the needs, preferences, and well-being of citizens. Unlike traditional top-down approaches, this concept ensures that smart city innovations are inclusive, accessible, and aligned with the priorities of the community.
Core Principles of Citizen-Centric Design in Smart City Concept
- Inclusivity.
- Engagement and Participation, while citizens are involved in decision-making processes through tools like online polls, forums, and mobile apps.
- Simplicity and Accessibility.
- Sustainability and Livability, when urban systems are designed to enhance the quality of life through cleaner air, safer neighbourhoods, and reduced commute times, creating environments where residents can thrive.
- Data Privacy and Security.
Through technologies like Video Surveillance as a Service (VSaaS), Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and BD analytics, smart cities are creating safer sustainable environment. They used to meet the needs of modern society. Here’s a closer look at the purpose of smart cities, the problems they solve, the technology that powers them, and examples of their positive impact worldwide.
Key Drivers Behind Smart City Implementation
Urban centres worldwide are grappling with a range of issues that impact citizens’ well-being, city economies, and the environment:
- Crime and Public Safety Risks. High population density and economic disparity leads to increased crime rates, theft, vandalism, and kidnapping. Cities must find ways to prevent crime proactively, respond to incidents quickly, and improve citizens’ sense of security.
- Traffic Congestion and Accidents. Growing urban populations intensify traffic congestion, leading to long commute times, high fuel consumption, and frequent accidents. Congestion not only impacts the environment but also hinders economic productivity and residents’ quality of life.
- Environmental Challenges. Urbanisation puts immense pressure on natural resources, contributing to pollution, excessive energy consumption, and waste generation. Cities need efficient solutions to reduce emissions, and promote greener practices.
How VSaaS and other technologies solves the problems in Smart City Concept
Smart cities aim to address these issues through innovative, data-driven solutions that make urban life safer, more efficient, and more sustainable. Technologies like Video Surveillance as a Service (VSaaS), IoT, and big data analytics play pivotal roles in transforming cities into more efficient, safe, and livable spaces. While governments, technology companies, and civic organisations remain essential contributors, internet providers (ISPs) and telecommunications companies (telcos) have emerged as the primary drivers behind the scalability and functionality of smart cities.
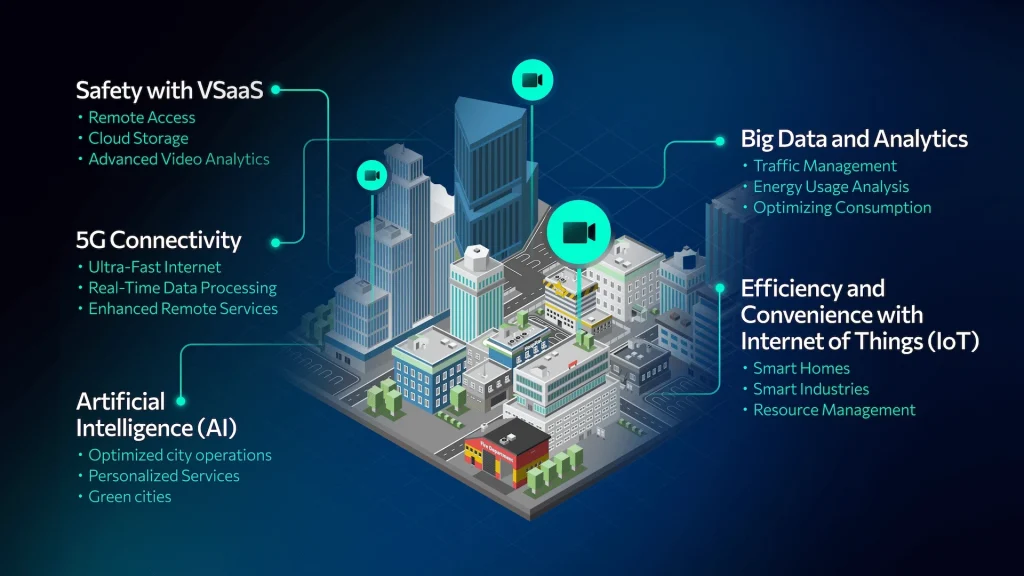
Below are several ways in which VSaaS and complementary technologies solve key problems faced by modern cities:
- VSaaS (Video Surveillance as a Service). VSaaS is integral to modern smart city systems, offering scalable, cloud-based video surveillance. Through VSaaS, video data from security cameras is stored in the cloud, accessible remotely, and shared across government agencies. With advanced analytics, VSaaS provides predictive insights into crime, traffic, and other urban activities. This allows authorities to respond proactively to emerging threats.
- Internet of Things (IoT). IoT devices connect various elements within a city — including vehicles, traffic lights, and sensors — to gather data and automate processes. IoT enables real-time monitoring of city services and facilitates dynamic responses to changing conditions, like adjusting traffic lights based on congestion.
- Big Data and Analytics, by collecting and analysing large volumes of data, smart cities can better understand urban patterns and resource demands. For example, analysing traffic and energy usage data helps optimise infrastructure and forecast needs, leading to more efficient resource management.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI). AI powers many smart city applications. They cover from analysing video footage for public safety to predicting traffic patterns and managing energy distribution. AI also enhances surveillance capabilities, helping detect potential threats and make informed, data-driven decisions.
- 5G Connectivity. With high-speed, low-latency networks, 5G supports the real-time data transfer that smart cities require. It enables instantaneous communication between IoT devices, ensuring timely responses and improving service reliability.
Positive Impact of VSaaS and Other Telco-Driven Innovations
Crime Prevention and Safety Measures
The Smart cities technology implements Video Surveillance as a Service (VSaaS) and AI-driven analytics to monitor public spaces, detect suspicious behaviour, and alert authorities to potential threats in real-time. Analysing video data and identifying patterns proactively prevent crime and investigate incidents efficiently. In regions prone to risks like kidnapping, VSaaS-equipped smart cameras with facial recognition can monitor high-risk areas, helping authorities respond swiftly to emergencies.
Traffic Management and Accident Prevention
Innovative smart traffic systems powered by IoT and AI enable real-time monitoring and management of traffic flow. Traffic lights, cameras, and sensors work together to adjust signal timings, reducing congestion and smoothing traffic movement. These systems can also detect accidents, alerting emergency services and rerouting traffic to minimise disruptions. While optimising transportation infrastructure, cities improve mobility and reduce emissions.
Energy Efficiency and Waste Management
Modern smart cities rely on smart grids for efficient energy distribution, enabling the integration of renewable energy sources and reducing overall consumption. Smart waste management systems use sensors to detect when bins are full, creating efficient collection routes that save fuel and reduce emissions.
Examples of Smart Cities and Their Positive Impact
Several cities worldwide have implemented smart city technologies with remarkable results:
Zurich, Switzerland
Zurich is a leading smart city known for its tech innovation, sustainability, and high quality of life. The city excels in digital services, green energy, efficient public transport, and eco-friendly urban planning. Its smart mobility solutions and transparent e-governance enhance urban living. Zurich also prioritises health tech, making it a model for sustainable, tech-driven cities.
Singapore
Known for its Smart Nation program, Singapore has deployed autonomous vehicles, digital identification systems, and a comprehensive urban dashboard that monitors various city metrics. These initiatives have improved traffic flow, enhanced safety, and supported efficient resource allocation.
Barcelona, Spain
Barcelona’s IoT-enabled water, lighting, and waste management systems have significantly reduced energy consumption and waste overflow. The city’s centralised IoT platform allows real-time coordination across services, creating a cleaner, more efficient environment for residents.
Dubai, UAE
Dubai’s Smart City initiative includes blockchain-powered government services, enhanced mobility solutions, and IoT-based monitoring for utilities and public safety. By connecting these elements, Dubai aims to provide seamless urban services, promote economic growth, and increase public safety.
Amsterdam, Netherlands
Amsterdam uses smart traffic lights and bike lanes to reduce congestion and promote sustainable transportation. The city’s environmental sensors also track air quality and emission levels, helping guide policies for a healthier environment.
Summarising. Global Development of Smart Cities: Plans for the Future
Smart cities are advancing rapidly as new technologies continue to evolve, paving the way for more ambitious and innovative plans for urban development. One of the most important areas of future development is in public safety and crisis management. By further integrating Video Surveillance as a Service (VSaaS) with AI and predictive analytics, smart cities are working to create highly responsive, preemptive systems. They detect patterns of behavior associated with potential crimes or security threats. This predictive approach aims to identify and address risks before incidents occur, making urban areas much safer. Advanced surveillance networks, combined with AI-driven insights, allow for immediate response coordination and the ability to prevent incidents proactively, thereby enhancing overall public security in increasingly complex urban environments.
Environment and Sustainability in Smart City
Another major focus of smart city development is achieving zero-emission targets. With many cities now committing to ambitious goals for carbon reduction, future smart city infrastructure is expected to play a critical role in achieving these targets. Smart grids will facilitate efficient, balanced energy distribution, while also supporting the integration of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. In addition to this, city-wide energy monitoring systems will help regulate consumption. It identifies inefficiencies, and promote sustainable practices among residents and businesses, all contributing to a significant reduction in the city’s carbon footprint. This commitment to zero-emission development reflects a broader effort to make cities healthier and more sustainable for future generations.
Public Health in Smart City
In the area of citizen engagement and public health, smart cities are also placing a strong emphasis on making services more accessible, inclusive, and responsive to residents’ needs. Public health monitoring systems, often supported by IoT-enabled devices, are allowing cities to track health trends and detect potential public health issues early. Remote healthcare options are becoming more integrated within smart city plans, giving citizens greater access to health services and support. Additionally, citizen engagement applications are gaining popularity. This enables residents to report issues directly to local government, access a variety of city services in one place, and participate actively in decision-making processes. This two-way communication strengthens the relationship between residents and city administration. It causes more trust and a sense of community while ensuring that the city can adapt quickly to the needs and concerns of its population.
Conclusion of Smart City Concept Development
Through these forward-looking initiatives in public safety, environmental sustainability, and citizen engagement, the next generation of smart cities will not only tackle immediate challenges. They also foster safer, greener, and more connected urban environments that improve the quality of life for all residents.
In conclusion, smart cities represent a significant step forward in urban planning and development, offering powerful solutions to the complex challenges of modern urban life. Through VSaaS, IoT, AI, and other advanced technologies, smart cities not only address immediate problems like crime and congestion. They also pave the way for a sustainable, prosperous future for generations to come.
Start your Aipix journey with expert guidance — reach out for a free consultation.





